Playbook.io Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
This project was built upon the AddressBook-Level3 (AB3) codebase provided by the National University of Singapore’s CS2103T Software Engineering module.
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
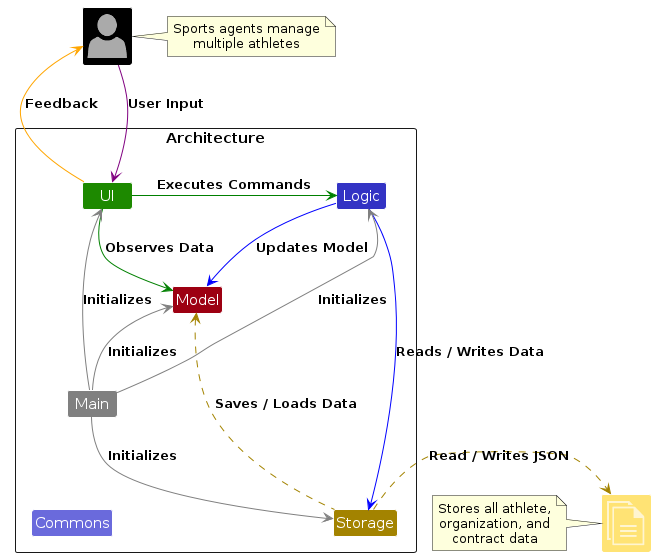
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in
charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
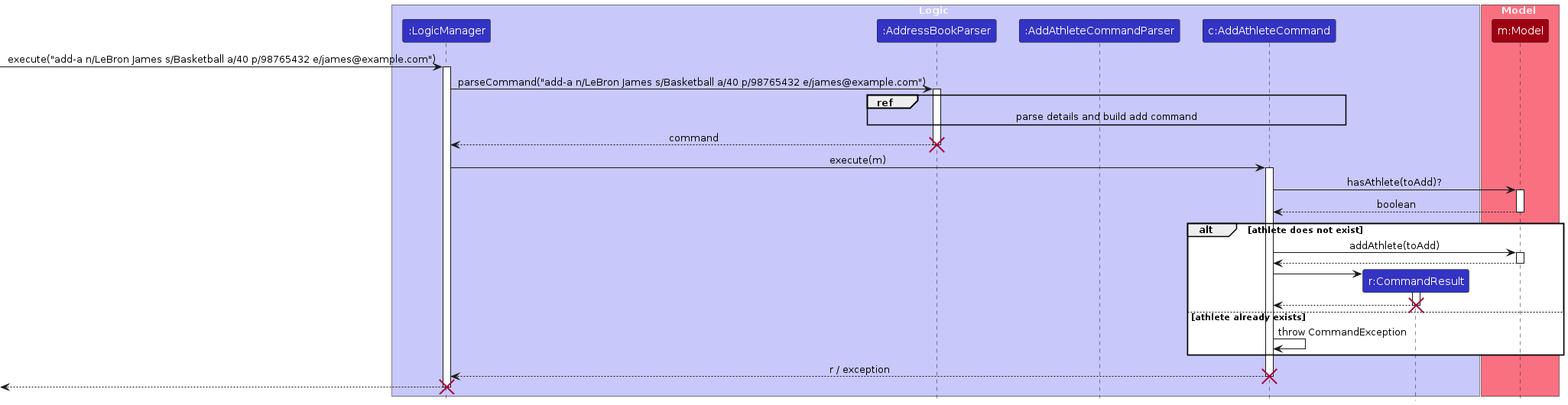
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues
the command delete-a n/LeBron s/Basketball.
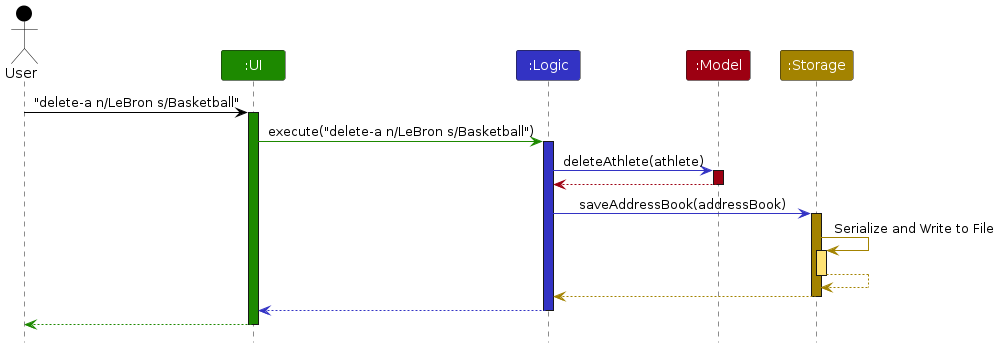
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point).
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using
the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface.
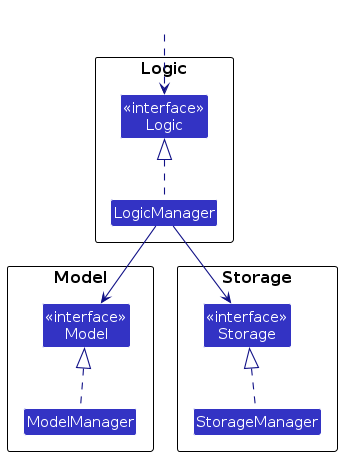
Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to
prevent outside components from being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial)
class diagram below.
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
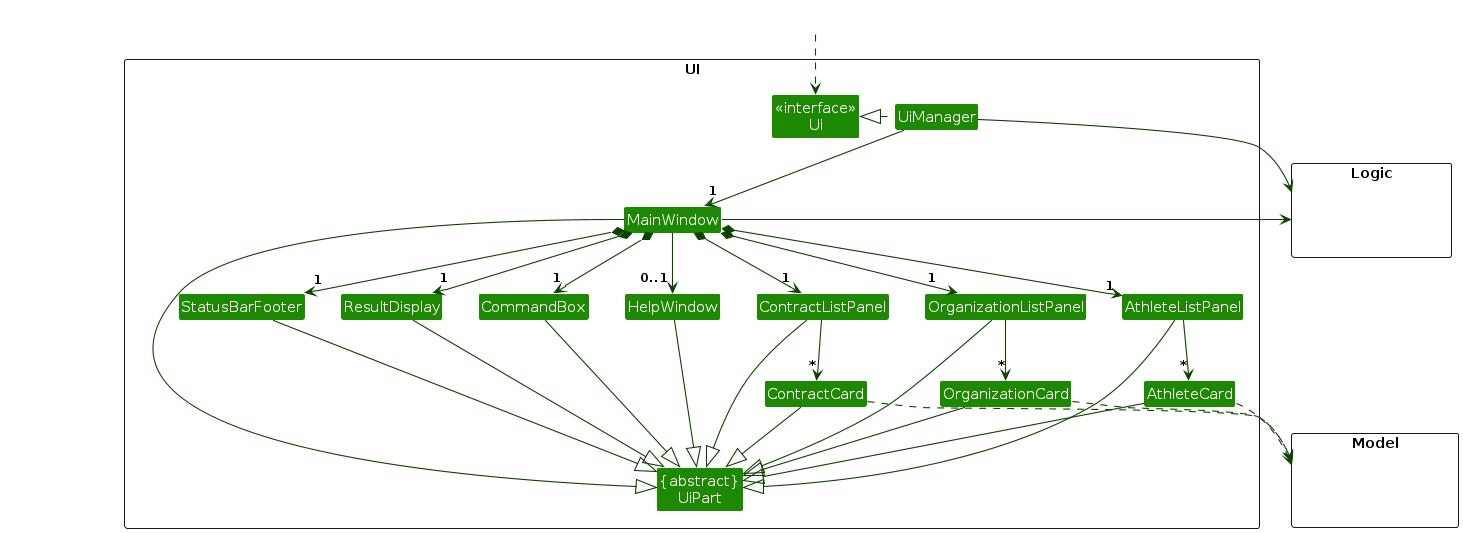
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g. CommandBox, ResultDisplay, AthleteListPanel,
OrganizationListPanel, ContractListPanel, StatusBarFooter, etc.
All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between
classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFX UI framework.
The layout of these UI parts is defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder.
For example, the layout of the MainWindow
is specified in MainWindow.fxml.
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysAthlete,Organization, andContractobjects residing in theModel.
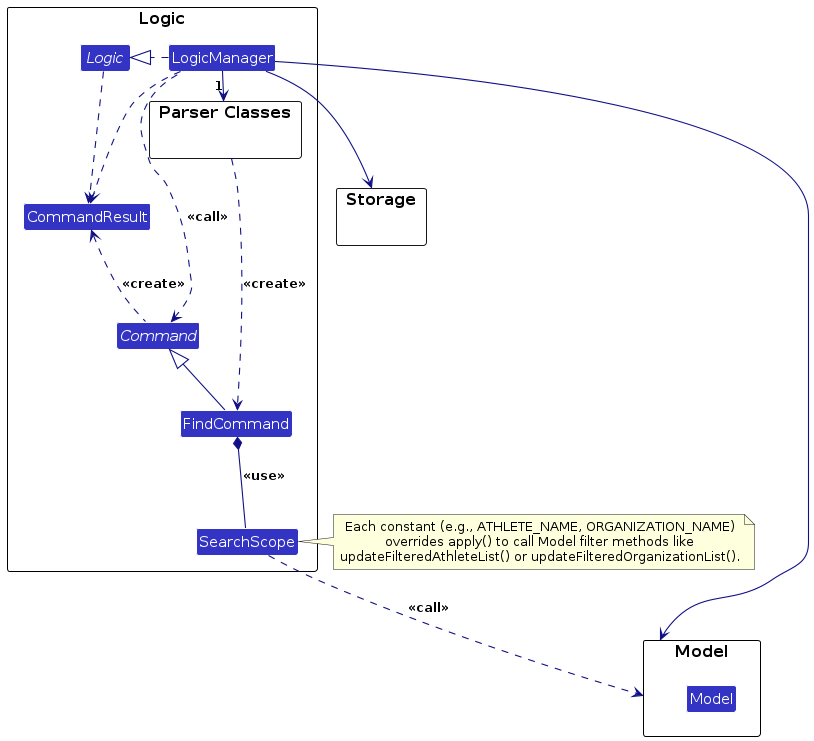
Logic component
API : Logic.java
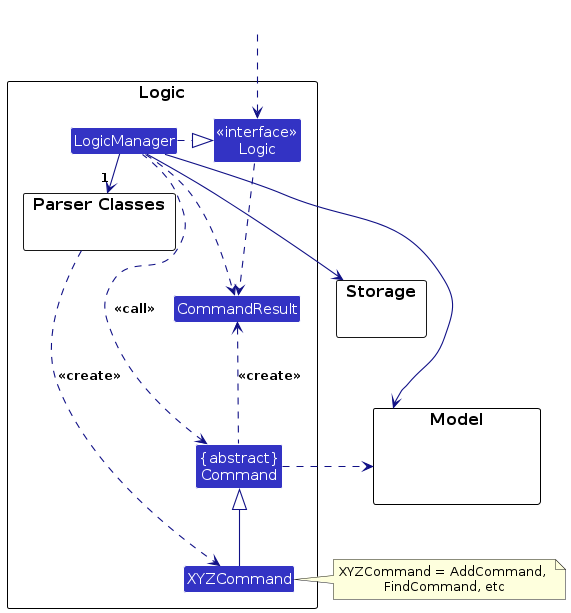
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
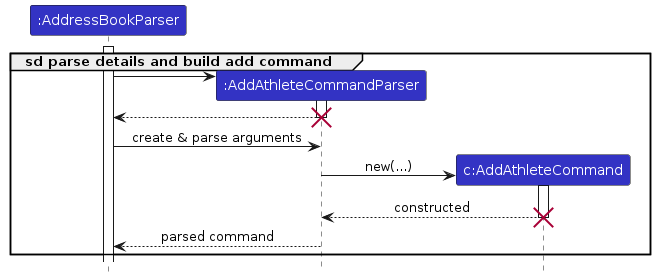
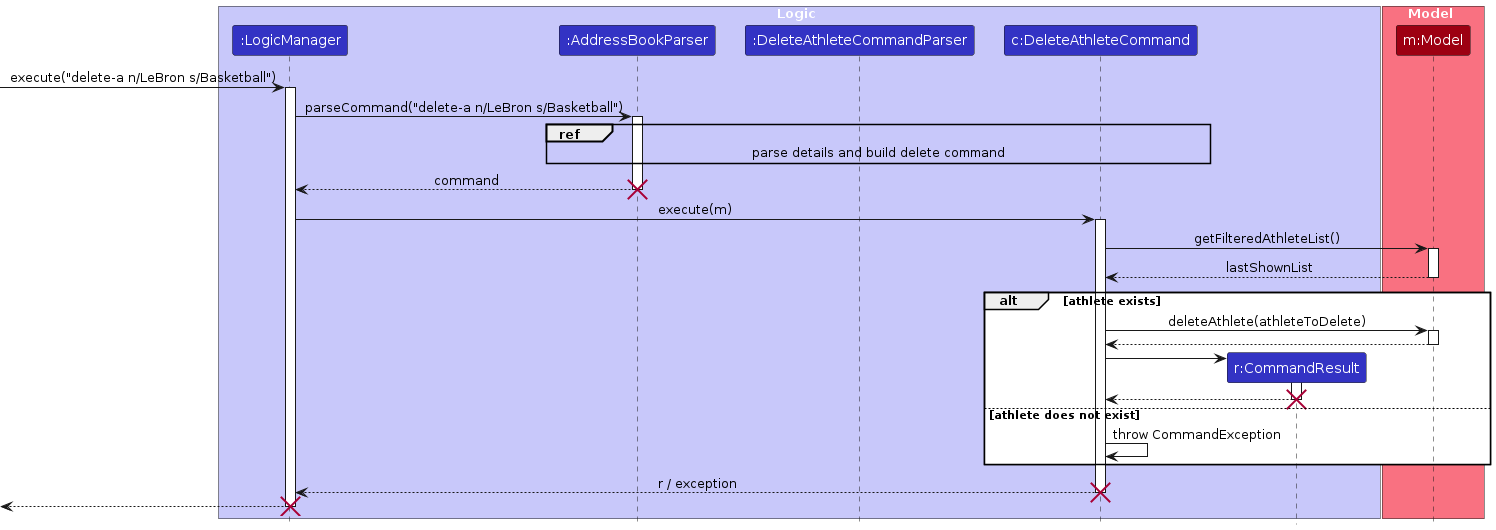
The sequence diagrams below illustrate the interactions within the Logic component,
taking the add-a and delete-a commands as examples.
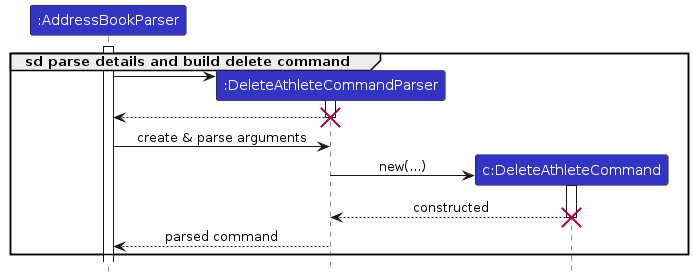
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it passes the user input to anAddressBookParserobject, which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,AddAthleteCommandParserorDeleteAthleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an instance of one of its subclasses such asAddAthleteCommandorDeleteAthleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command communicates with the
Modelwhen executed (e.g., to add or delete an athlete). Although this is shown as a single step in the diagrams above for simplicity, the actual implementation involves multiple interactions between theCommandand theModel. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject, which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing user commands:
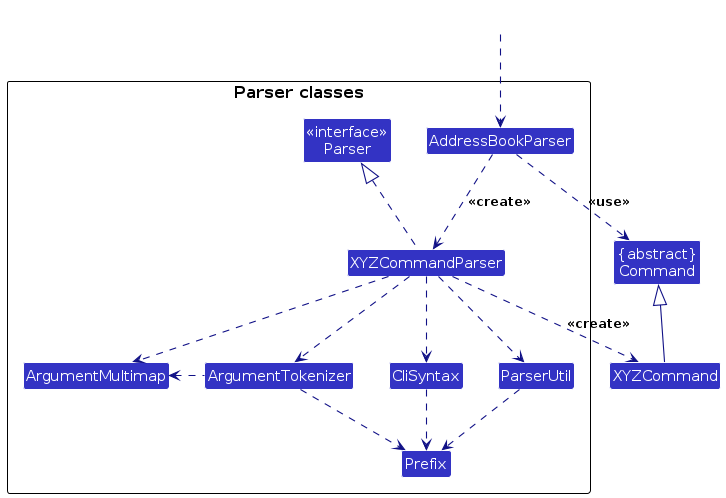
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name, e.g.,AddAthleteCommandParser,AddOrganizationCommandParser,AddContractCommandParser,DeleteAthleteCommandParser, etc.), which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create anXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddAthleteCommand). - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddAthleteCommandParser,DeleteAthleteCommandParser,AddOrganizationCommandParser) implement theParserinterface so that they can be treated uniformly (e.g., during testing).
Model component
API : Model.java
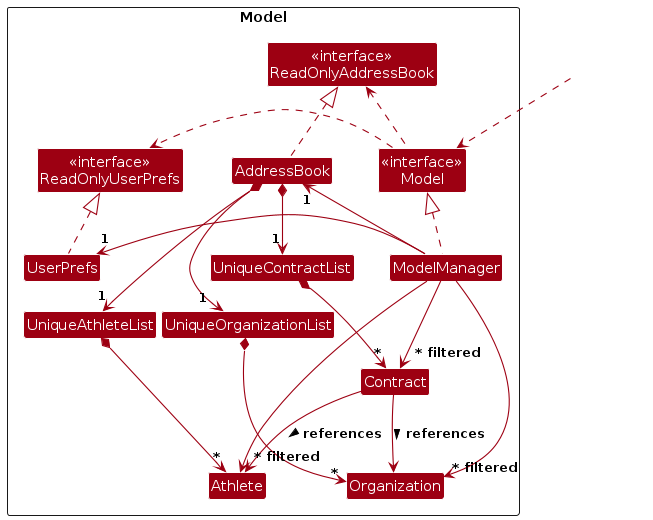
The Model component,
- stores the application data — i.e., all
Athlete,Organization, andContractobjects, which are contained inUniqueAthleteList,UniqueOrganizationList, andUniqueContractListobjects respectively. - stores the currently “selected” data (e.g., results of a search query) as separate filtered lists, which are exposed
to the outside as unmodifiable
ObservableList<>objects (for example,ObservableList<Athlete>). This allows the UI to automatically update when the underlying data changes. - stores a
UserPrefsobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefsobject. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents domain data that should make sense independently of other layers).
Storage component
API : Storage.java
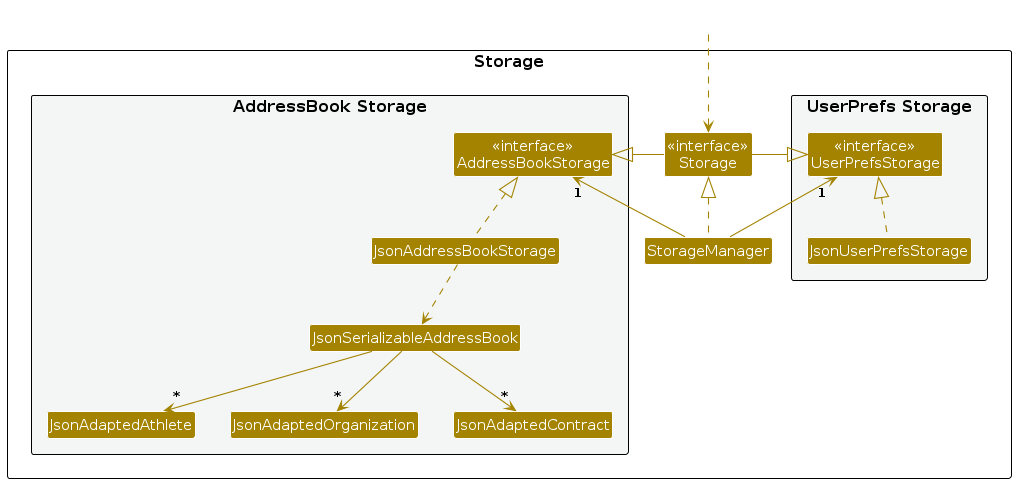
The Storage component,
- can save both application data (including
Athlete,Organization, andContractinformation) and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects. - inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefsStorage, which means it can be treated as either one if only the functionality of one is needed. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save and retrieve objects that belong to theModel.
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.address.commons package.
Data Types and Overflow Protection
Contract Amount Handling
The application has been designed to handle large contract amounts that are common in professional sports:
- Data Type: Contract amounts use
longintegers (64-bit) instead ofint(32-bit) - Maximum Value: Up to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (approximately 9.2 quintillion)
- Limit Applied: Both individual contract amounts and total contract amounts for an athlete or organization cannot exceed this maximum value
- Overflow Protection: The
ensureNoTotalOverflow()method validates total contract amounts using predicate-based filtering and checks both athlete and organization totals before adding new contracts - Validation Logic: Uses
sumForPredicate()to calculate current totals andwouldOverflow()to detect if adding a new contract would exceed the maximum limit - UI Display: Contract totals are properly formatted using
NumberFormatfor large amounts
Why long Instead of int
- Real-world Requirements: Professional sports contracts can exceed $2 billion (
intlimit: ~2.1 billion) - Cumulative Totals: Popular athletes/organizations can have total contracts exceeding
intlimits - Future-proofing: Protects against inflation and larger contract values
- Error Prevention: Eliminates negative overflow display bugs in UI chips
Implementation
This section describes noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
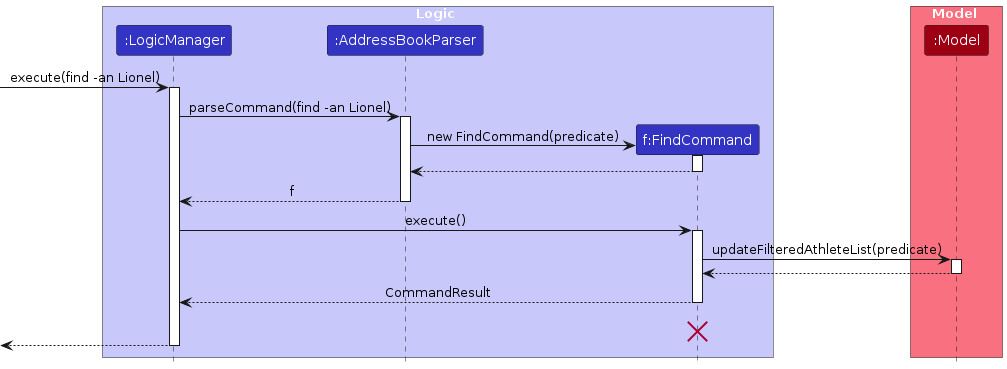
[Implemented] Find command
The Find command enables users to perform keyword-based searches across different data types within the system —
athletes, organizations, and contracts — using flexible, case-insensitive, and fuzzy matching.
It temporarily filters the displayed lists in memory without altering any saved data.
The FindCommand extends Command and is invoked with one required flag that specifies the search scope.
The following flags are supported:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
-an | Finds athletes by name |
-as | Finds athletes by sport |
-on | Finds organizations by name |
-ca | Finds contracts by athlete name |
-co | Finds contracts by organization name |
-cs | Finds contracts by sport |
Example usage:
find -an Lionel
Upon execution, the command:
- Validates that exactly one flag is present.
- Extracts the keyword and normalizes it to lowercase.
- Delegates filtering to an appropriate method in
Model, depending on the flag. - Applies a multi-tier fuzzy-matching predicate combining substring and Levenshtein-distance checks.
- Constructs a
CommandResultreporting how many entities matched.
Search scopes and behavior
Each flag maps to a SearchScope enum constant that defines:
- A label (e.g., “athletes”, “organizations”, “contracts”)
- The
UiTabto display in the interface - A custom
apply(Model, keyword)implementation that calls the relevant model filter
This enum-based design ensures that each scope encapsulates its filtering logic neatly within a single override, improving maintainability and readability.
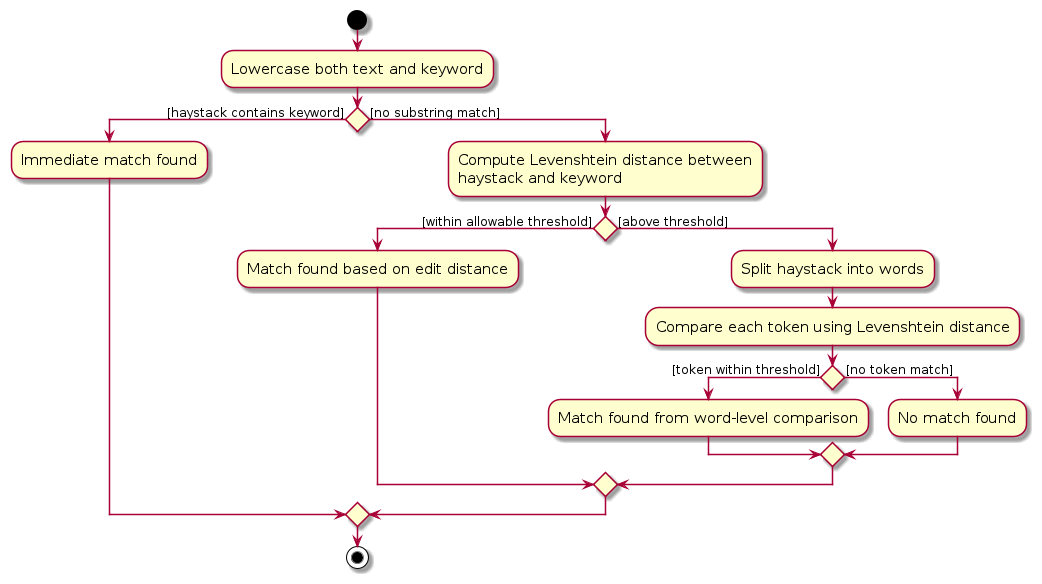
Matching logic
The matching mechanism performs three-tier Levenshtein-based fuzzy matching implemented within the command itself:
- Exact substring check — returns a match if the keyword appears as a case-insensitive substring.
- Full-text Levenshtein match — compares the entire field value against the keyword, allowing a small number of edits based on keyword length.
- Word-by-word Levenshtein match — splits the text into words and matches each token individually.
This approach allows tolerant and human-friendly searches (e.g., find -an leo matches “Lionel Messi”;
find -co arsnal matches “Arsenal”).
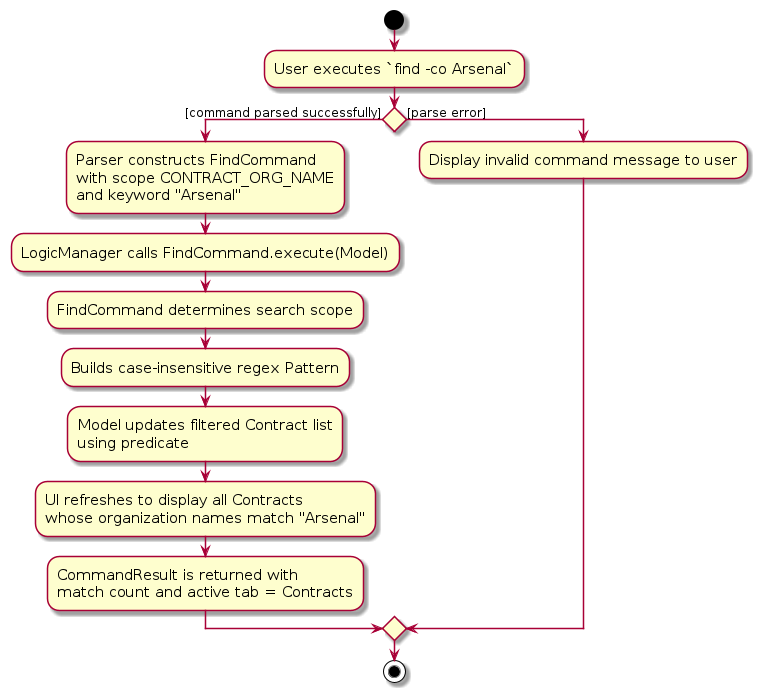
Example flow
The following scenario demonstrates how a typical command executes:
Step 1. The user executes find -co Arsenal.
Step 2. The parser constructs a FindCommand with scope CONTRACT_ORGANIZATION and keyword Arsenal.
Step 3. The command invokes model.updateFilteredContractList(predicate).
Step 4. The UI’s observable list updates, displaying all contracts linked to organizations matching “Arsenal”.
Step 5. A CommandResult reports the number of matching contracts and switches the active tab to Contracts.
Design considerations
Aspect: How search scope is determined
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Use an enum (
SearchScope) with one method per scope.- Pros: Compact, type-safe, easily extensible for new scopes.
- Cons: Slightly more complex when flags overlap semantically.
- Alternative 2: Use a single switch statement on the flag.
- Pros: Simple and direct for small command sets.
- Cons: Harder to extend; increases method size.
Aspect: Matching method
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Custom Levenshtein-based fuzzy match with multi-tier logic.
- Pros: Natural partial and typo-tolerant matches without external libraries.
- Cons: Slightly higher computational cost on large datasets.
- Alternative 2: Simple exact or tokenized substring match.
- Pros: Faster and easier to reason about.
- Cons: Misses partial and typo-tolerant results.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- sports agents who manage multiple athletes and their careers
- need to stay organized with many organizations (teams, sponsors, brands)
- prefer structured tools over manual spreadsheets or scattered files
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefer typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: The ultimate platform that empowers sports agents to stay organized, build stronger relationships, and drive success for their athletes and partners.
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | new user | see usage instructions | refer to instructions when I forget how to use the App |
* * * | sports agent | create a new athlete profile | keep track of the athletes I currently represent |
* * * | sports agent | delete an athlete profile | remove athletes I no longer represent |
* * * | sports agent | create a new organization | store details of teams, sponsors, or brands I work with |
* * * | sports agent | delete an organization | remove organizations that are no longer relevant |
* * * | sports agent | upload a new contract | track my athletes’ active agreements |
* * * | sports agent | delete a contract | keep my records up to date |
* * | sports agent | search for an athlete, organization, or contract | quickly find the information I need without scrolling |
* * | sports agent | edit an athlete's profile information | update their details as their career progresses |
* * | sports agent | edit an organization's information | keep organization details current and accurate |
* * | sports agent | edit a contract's information | keep contract details current and accurate |
* * | sports agent | sort contracts by amount | identify the most valuable deals quickly |
* * | sports agent | export contract data | share reports with clients or use in other applications |
* | sports agent | view analytics on contracts & deals | gain insights into performance and opportunities |
* | sports agent | link travel plans to competition and appearance schedules | coordinate logistics efficiently and avoid scheduling conflicts |
* | sports agent | manage and sync my athletes’ competition schedules and training events in a central calendar | coordinate effectively with teams, sponsors, and travel arrangements |
* | sports agent | set reminders for contract renewal dates | never miss important negotiation windows |
* | sports agent | track payment schedules within contracts | ensure timely payments and cash flow management |
* | sports agent | compare multiple contracts side by side | make informed decisions during negotiations |
* | sports agent | attach documents to contracts | keep all related paperwork in one place |
* | sports agent | receive notifications for contract milestones | stay informed of important contract events automatically |
* | sports agent | track commission earned from each contract | manage my own finances and business performance |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the playbook.io and the Actor is the user, unless specified
otherwise)
Use case: Add Athlete Profile
MSS
Agent requests to add athlete
playbook.io creates and stores the new athlete profile
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. Duplicate athlete
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete Athlete Profile
MSS
Agent requests to delete athlete
playbook.io deletes the athlete profile
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No athlete found
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2b. Athlete has active contracts
2b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Add Organization Profile
MSS
Agent requests to add organization
playbook.io creates and stores the new organization profile
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a Duplicate organization
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete Organization
MSS
Agent requests to delete an organization
playbook.io deletes the organization profile
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No organization found
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2b. Organization has active contracts
2b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Add Contract
MSS
Agent requests to add contract
playbook.io creates and stores the new contract
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. Athlete does not exist
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2b. Organization does not exist
2b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2c. Duplicate contract
2c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete Contract
MSS
Agent requests to delete a contract
playbook.io deletes the contract
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No contract found
2a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Find Athlete
MSS
Agent requests to find an athlete, specifying either the athlete’s name or sport as a parameter
playbook.io returns the list of athletes
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No athlete found
2a1. playbook.io returns an empty list
Use case ends.
Use case: Find Organization
MSS
Agent requests to find an organization, , specifying the organization’s name
playbook.io returns the list of organization
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No organization found
2a1. playbook.io returns an empty list
Use case ends.
Use case: Find Contract
MSS
Agent requests to find a contract, specifying either the athlete’s name, sport, or organization’s name as a parameter
playbook.io returns the list of contracts
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1b. Missing required parameter
1b1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
1c. The given parameter is invalid
1c1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
2a. No contract found
2a1. playbook.io returns an empty list
Use case ends.
Use case: Refresh Data
MSS
Agent requests to refresh to clear any active search filters
playbook.io returns the latest lists of athletes, organizations, and contracts.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: View Help Information
MSS
Agent requests to open the help window
playbook.io opens the help window
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Use case: Close Session
MSS
Agent requests to exit the system
playbook.io closes the session
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. The given command is invalid
1a1. playbook.io shows an error message
Use case ends.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
17or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 athletes, organizations, and contracts without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should validate all input data (e.g., names, emails, dates, amounts) and provide clear error messages when invalid input is detected.
- Should allow the application to be packaged and distributed in a portable format (e.g., JAR or Docker container) for ease of deployment across environments.
- Should allow a new user to learn the system within 10 minutes by following the user guide.
- Should provide consistent response times (<2 seconds) for retrieval commands such as searching athletes, organizations, or contracts under normal usage load.
- Should prevent duplicate records by enforcing unique key constraints (e.g., same athlete name + sport).
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- Athlete: An individual sports performer managed by the agent, with contact details and sport specialization.
- Contract: A business agreement between an athlete and organization, including financial terms and duration.
- Fuzzy Search: A search method that finds results even with typos or partial matches, using intelligent algorithms.
- Organization: Any business entity that contracts with athletes - teams, sponsors, agencies, brands, etc.
- Sports Agent: A professional who represents athletes in contract negotiations and career management.
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
1. Initial launch
- Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder.
- Double-click the jar file.
Expected: Shows the GUI. The window size may not be optimum.
2. Saving window preferences
- Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
- Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Adding an athlete
1. Adding an athlete while all athletes are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Athletes Tab by pressing Cmd+1 (or Ctrl+1 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
add-a n/Lebron James s/Basketball a/40 p/99876543 e/James@example.com
Expected: Athlete is added to the athlete list. Details of the added athlete shown in the result pane. - Test case:
add-a n/ s/Football a/39 p/87654321 e/cr7@example.com
Expected: No athlete is added. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect add-a commands to try:
add-a,add-a n/Messi2 s/Football a/39 p/87654321 e/cr7@example.com,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting an athlete
1. Deleting an athlete while all athletes are being shown
- Prerequisites:
- Switch to the Athletes Tab by pressing Cmd+1 (or Ctrl+1 on Windows/Linux).
- Ensure the athlete to be deleted has no existing contracts.
- Test case:
delete-a n/Lebron James s/Basketball
Expected: Athlete is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted athlete shown in the result pane. - Test case:
delete-a n/Lebron James s/
Expected: No athlete is deleted. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect delete-a commands to try:
delete-a,delete-a n/Lebron James s/Basket-ball,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding an organization
1. Adding an organization while all organizations are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Organizations Tab by pressing Cmd+2 (or Ctrl+2 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
add-o o/Nike p/98765432 e/partnerships@nike.com
Expected: Organization is added to the organization list. Details of the added organization shown in the result pane. - Test case:
add-o o/Nike p/+6598765432 e/partnerships@nike.com
Expected: No organization is added. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect add-o commands to try:
add-o,add-o o/Nike123 p/98765432 e/partnerships@nike.com,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting an organization
1. Deleting an organization while all organizations are being shown
- Prerequisites:
- Switch to the Organizations Tab by pressing Cmd+2 (or Ctrl+2 on Windows/Linux).
- Ensure organization to be deleted has no existing contracts.
- Test case:
delete-o n/Nike
Expected: Organization is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted organization shown in the result pane. - Test case:
delete-o n/
Expected: No organization is deleted. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect delete-o commands to try:
delete-o,delete-o n/Nike1,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Adding a contract
1. Adding a contract while all contracts are being shown
- Prerequisites:
- Switch to the Contracts Tab by pressing Cmd+3 (or Ctrl+3 on Windows/Linux).
- Ensure the athlete and organization exist in the system.
- Test case:
add-c n/LeBron James s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/01012025 am/50000000
Expected: Contract is added to the contracts list. Details of the added contract shown in the result pane. - Test case:
add-c n/LeBron James s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/01012025 am/
Expected: No contract is added. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect add-c commands to try:
add-c,add-c n/LeBron James s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/01012025 am/50.90,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting a contract
1. Deleting a contract while all contracts are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Contracts Tab by pressing Cmd+3 (or Ctrl+3 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
delete-c n/LeBron James s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/01012025 am/50000000
Expected: Contract is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contract shown in the result pane. - Test case:
delete-c n/LeBron James s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/ am/50000000
Expected: No contract is deleted. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect delete-c commands to try:
delete-c,delete-c n/ s/Basketball o/Nike sd/01012024 ed/01012025 am/50000000,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Finding an athlete
1. Finding an athlete while all athletes are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Athletes Tab by pressing Cmd+1 (or Ctrl+1 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
find -an LeBron James
Expected: Filtered list of athletes shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -as Basketball
Expected: Filtered list of athletes shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -an
Expected: No filtering occurs. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect find commands to try:
find -as,find,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Finding an organization
1. Finding an organization while all organizations are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Organizations Tab by pressing Cmd+2 (or Ctrl+2 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
find -on Nike
Expected: Filtered list of organizations shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -on
Expected: No filtering occurs. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect find commands to try:
find,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Finding a contract
1. Finding a contract while all contracts are being shown
- Prerequisites: Switch to the Contracts Tab by pressing Cmd+3 (or Ctrl+3 on Windows/Linux).
- Test case:
find -ca LeBron James
Expected: Filtered list of contracts shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -cs Basketball
Expected: Filtered list of contracts shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -co Nike
Expected: Filtered list of contracts shown. Details of the filtered list shown in the result pane. - Test case:
find -ca
Expected: No filtering occurs. Error details shown in the result pane. - Other incorrect find commands to try:
find -cs,find -co,...
Expected: Similar to previous.
Saving data
1. Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
1.1 Simulate a missing file
- Close playbook.io.
- Navigate to the
datafolder. - Delete one or more JSON files (e.g.,
athletelist.json,contractlist.json,organizationlist.json). - Re-launch playbook.io.
Expected:
- If
contractlist.jsonis not empty but one or more of the other files are missing, all JSON files are re-generated as empty lists. - Otherwise, only the missing files are automatically generated as empty lists.
1.2 Simulate a corrupted file
- Open a JSON file (e.g.,
athletelist.json). - Add invalid content (e.g., remove a closing bracket or insert invalid characters).
- Save the file and relaunch playbook.io.
Expected: The app detects that the files are corrupted and loads empty lists for all entities.
⚠️ Important: New JSON files are only created once data is written (e.g., after adding an athlete, contract, or organization).
2. Normal save
2.1 Simulate saving data after adding entries
- Open playbook.io.
- Add an athlete, contract, or organization
- Close playbook.io.
Expected: Data is persisted correctly in the JSON files.